An Attractive Alternative to Selling the Company
Private-to-Public Equity (PPE)™ Business Combination Initiative
An Attractive Alternative to Selling the Company
When owners of late stage private companies contemplate exit options, the most obvious option for them is to sell the company in exchange for cash and equity returns. While a sale may seem the most straight forward and simplest, a sale will bring in uncertainties in almost every aspect of a company, not the least will be in the operational control and the management structure. When owners’ interests are not aligned with that of current management team, owners will usually push for favorable exit terms and valuation, instead of focusing on long-term growth synergies and the greater potential return. As such, it will be difficult for the company and the employees to achieve optimal benefits from the sale. In comparison, becoming a public company by merging with a PPETM/Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC) has become an attractive alternative, more so when the executive team is committed to growing the company via organic growth or M&As to an unicorn status.
For those who are not familiar with the SPAC concept, it can basically be described as follows:
- The SPAC entity, sometimes referred to as a “blank check” company, is first formed by an investor group of experienced and qualified investors and business professionals.
- The SPAC then undergoes the typical initial public offering (IPO) process, whereby the company is listed on a major US exchange, receives a “ticker” on that exchange, raises capital and starts market trading. The entire process, exactly as in the standard IPO process, is tightly controlled and regulated by the SEC rules.
- Immediately after successful completion of the IPO process, the SPAC entity, which has a limited time duration before expiration and dissolving itself (typically 18-24 months), launches a search process to identify an appropriate target company, engages in negotiating a definitive agreement to merge with that company using the “reverse merger” mechanism and implements the merger, typically within 6-9 months after the execution of the definitive agreement.
- The result is that the target company becomes listed on a major US stock exchange under a new “ticker” symbol and has full access to the public capital market.
- Additionally, the company typically enjoys an infusion of cash at the closing of the combination.
 Overall, this process provides the target company a faster and lower risk path to become a publicly listed entity with less disturbance to the on-going operations of the company and its strategic growth plans. Further, as compared to a traditional IPO process, the PPE/SPAC process significantly reduces the management time and attention required to achieve public company status. In many ways, the PPE process can be characterized as “an IPO in box”.
Overall, this process provides the target company a faster and lower risk path to become a publicly listed entity with less disturbance to the on-going operations of the company and its strategic growth plans. Further, as compared to a traditional IPO process, the PPE/SPAC process significantly reduces the management time and attention required to achieve public company status. In many ways, the PPE process can be characterized as “an IPO in box”.
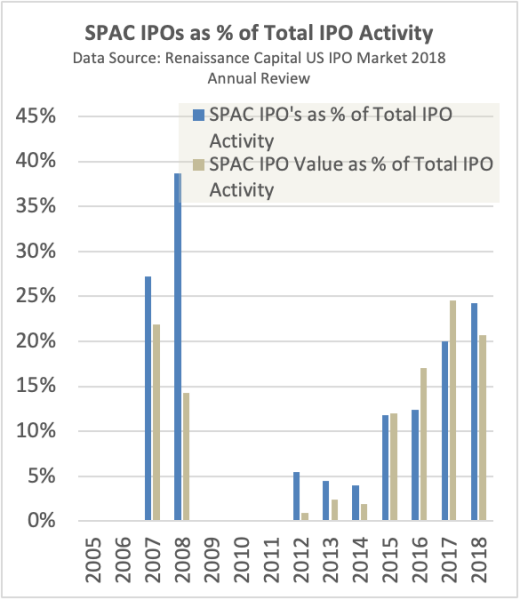
Because of its effectiveness in bring companies public, the SPAC process has gained significant interest from the financial community as evidenced by the recent growth in the number of SPAC offerings. There has been an upward trend in SPAC IPOs since 2011, in both deal count and dollar amount raised. In 2018, SPACs counted for 24% of total U.S. IPO deals and 21% of IPO dollar value. As of October 2019, there are 90 active SPACs, which raised total of $18 billion. Of this group, 20 have announced a combination target or have executed a share purchase agreement (SPA) with and expect to close the merger transaction shortly.
Why Consider a SPAC Transaction
SPACs typically address companies that are in late stage growth and have achieved financial parameters that support an Enterprise Values (EV) of $500 million or higher.
Compared to an outright sale, utilizing the SPAC process offers several significant advantages to the private company contemplating its exit options.
- Straightforward access to public capital market. The most obvious advantage of a SPAC is that it affords the target company a clear and more secure path to the public capital markets. A business combination with a SPAC guarantees a public listing (i.e. a “ticker”) and avoids the limitations of the “IPO window”, the risky pricing discovery process and the uncertainty in actually completing the offering that is associated with the traditional IPO process. Since the SPAC has completed an IPO and is already traded as a public company, the combination, since it is a “reverse merger” controlled by the SPAC entity, has a minimum and clearly understood risk of failing. Hence, the public listing of the target company is secured with a very high level of confidence.
- Ready access to public capital markets. Post the combination, the company has access to two valuable forms of currency. Namely, cash on the balance sheet and the ability to issue equity instruments to obtain additional financing of various sorts. This flexibility is a tremendous advantage for the company as it can provide either cash or equity to be used in strategic transactions (i.e. M&A) and use equity sales to strengthen its balance sheet. In comparison to PE funding, using the public currency for raising funds for the company can usually be less dilutive and avoids the strictures typically put on management in PE funding transactions. These points become even more important and critical in market segments that are undergoing fast consolidation, where timely acquisitions are necessary to secure rapid growth of the company. The company’s public currency can be deployed quickly and such transactions avoid the delays inherent in PE transactions.
- No future ownership uncertainty. Based on market condition, buyers in a sales transaction could be either strategic or financial (i.e. a private equity firm), and the uncertainty in the buyers introduces additional risks to the company. For financial buyers, the private equity funds commonly have a hold period of five to seven years in an active deal market, and they will exit all their investments before the fund liquidates. The relatively short sale cycle and constant ownership change make it difficult for a company to execute a long term strategic roadmap, and it will impact company’s valuation. In contrast, a SPAC transaction provides a known path to the public equity markets with the parameters of the transaction known in advance.
- Control over future stock. Comparing to an exit through a combination with a SPAC, owners who choose to sell the company to a strategic buyer essentially give up the upside potential of their stock in the public market, as they will lose control over future stock after the sale. Even though the sale might grant quicker return to the owners, the opportunity cost may be considerably higher. With an exit through the SPAC combination, the distribution of stock to the management team will help align their interests and motivate them to maximize the future growth post the combination.
- Retention of management control. In a SPAC transaction, the current management continues to lead the company and typically is supported by members of the SPAC sponsorship team who join the company as members of the Board of Directors or in other types of advisory positions. This type of involvement is more of an advisory and supportive partnership approach that is focused on the long-term stable and successful growth of the company to the benefit of all stakeholders, rather than highly focused on short-term ROI financial gains. This partnership theme is further motivated by the fact that the SPAC team, as significant shareholders in the business, see their financial upside based purely on the future enhanced equity value of the enterprise.
- Focus on long-term value creation. The key fiduciary duty of management in the now publicly traded company that has been created through the combination with the SPAC, is to achieve stable financial performance and generate long-term value. A SPAC transaction provides a vehicle for the founders, investors and management of the company to continue to build the business and implement their long term vision for the enterprise, thus providing enhanced value creation for all stakeholders. The aspect of motivation for long term value creation is missing in the event of strategic sale.
The Unique Advantages of Working with GigCapital
In addition to the aforementioned general advantages of a SPAC transaction noted above, the GigCapital team, which pioneered enhancing the traditional SPAC process with its Private-to-Public Equity (PPE)™ and Mentor-Investor™ approaches, provides a unique set of advantages and benefits to the target company. The GigCapital team is a very experienced group of entrepreneurs and executives comprised of former CEOs, senior-level corporate finance and SEC accounting executives, technical experts and industry renowned and respected thought-leaders that bring expertise and insights across all aspects of company management. It includes the complete spectrum of company leadership skills from product development and new product introduction (NPI), operations, sales and marketing, strategic planning and execution, private and public market financing, mergers and acquisitions, fund raising and wall-street connectivity, and global senior leadership level experience. As successful entrepreneurs and industry leading multinational corporation executives, the GigCapital partners provide a complete set of advisory expertise that may be needed by the target company as it enters the new stage of its growth as publicly traded companies.
Our unique approach to the SPAC transitional methodology is characterized by the following attributes:
- Ongoing support of the company through our Mentor-Investor™ involvement that typically includes providing expert Board of Director participation and Advisory Board participation.
- Providing an “IPO in a box” solution, which fundamentally brings all the required practices, connections, methodology, processes and knowhow to the IPO process, based on years of experience and numerous successful IPO transactions.
- Guidance and mentoring to management as they enter the public capital markets and start their journey in this unique environment.
- Leveraging our extensive investment banking relationships to assist the company in subsequent financing activities such as Private Investments in a Public Entity (PIPE), secondary offerings, debt financing, etc.
- Extensive experience in M&A transactions as a method to rapidly grow the business.
- Mentorship to senior management as they grow and develop the business and face the inevitable challenges associated with that growth. This mentorship focuses on enhancing the operation of the business and further unlocking the inherent value of the enterprise.
- Through our personal networks providing important introductions to industry leaders and executives on a worldwide basis, as well as investment banks, research analysts, institutional investors and debt lenders
Our PPE™ / M-I™ approach not only provides the key benefit of quickly becoming a publicly traded company through the SPAC methodology, but additionally, it is based on forming a true partnership with the company leadership and owners by providing assistance and guidance to assist in the development of the long term potential of the business.